The Ozark Mountains, a majestic and ancient range, stretch across the south-central United States, featuring a diverse landscape of heavily forested highlands and rugged terrain. The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Plateau or Ozark Highlands, span across five states – Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, Kansas, and Illinois – with the majority of the region falling within Southern Missouri and Northern Arkansas.
Understanding the age of the Ozark Mountains helps us appreciate their geologic history and the processes that have shaped the region over time. Although these mountains are not as tall as their counterparts in the Rockies or the Appalachians, the Ozarks have a unique and fascinating history that dates back hundreds of millions of years. Exploring the formation of this captivating geological region provides valuable insights into the intricate and dynamic nature of our planet’s evolution.
Formation and Geology of the Ozark Mountains
Geological History
The Ozark Mountains, also known as the Ozark Plateau, are located in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, and the extreme southeastern corner of Kansas. These mountains are among the oldest in the world, dating back to prehistoric times.
Formation Processes
Contrary to other mountain ranges, the Ozarks were primarily formed through erosion rather than folding and faulting. The rocks that comprise the Ozarks were initially sand, silt, and remains of marine animals which were laid down in a shallow sea at the beginning of the Paleozoic Era, approximately 542 million years ago.
Limestone
Limestone is a significant component of the Ozark Mountains’ geology. It is formed from the remains of marine organisms and is known for its ability to create caves and sinkholes. The Ozarks’ limestone is attributed to the shallow sea environment that existed during the Paleozoic Era.
Dolomite
Dolomite is another vital rock found in the Ozarks and is often associated with limestone. It is formed when magnesium replaces some of the calcium in limestone, providing it with a unique physical appearance and resistance to erosion. This mineral contributes to the structural stability of the Ozark Mountains.
Chert
Chert is a sedimentary rock, mainly composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz. It is found within the limestone and dolomite layers of the Ozark Mountains. Chert is known for its hardness and durability, which makes it suitable for tool-making by early inhabitants of the region.
Sandstone
Sandstone is another essential rock type found in the Ozark Mountains. Originating from the sand and silt deposits during the Paleozoic Era, sandstone contributes to the overall geology and landscape of the Ozarks. Its presence in the mountains indicates the varying environmental conditions that have shaped the area over time.
Topography and Landscape of the Ozarks
Elevation and Peaks
The Ozark Mountains, also known as the Ozark Highlands, span across the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, and Kansas source. Elevation in this region varies, with the highest peaks found in the Boston Mountains in Arkansas, many exceeding 2,000 feet (600 m) source. The Boston Plateau, which ranks as the tallest among the Ozarks, is characterized by higher precipitation and lower temperatures than other parts of the region due to its elevation source.
Plateaus and Highlands
The Ozark Highlands area is an extensive mountainous region with a coverage of between 47,000 square miles (122,000 km²) and 50,000 square miles (129,000 km²) source. The Ozarks can be divided into three main plateaus:
- Springfield Plateau: This area is relatively flat, with limestone and chert layers that provide a favorable condition for agriculture.
- Salem Plateau: Characterized by dolomite features and a karst topography, this plateau features various caves, sinkholes, and springs.
- Boston Plateau: As the highest among the three, its rugged terrain and high elevations create a unique landscape with various hills and mountains.
Karst Features and Caves
Ozark Mountains are well known for their karst topography, with features such as limestone caves, sinkholes, and springs source. This landscape is especially evident in the Salem Plateau, where dolomite formations contribute to the abundance of such features.
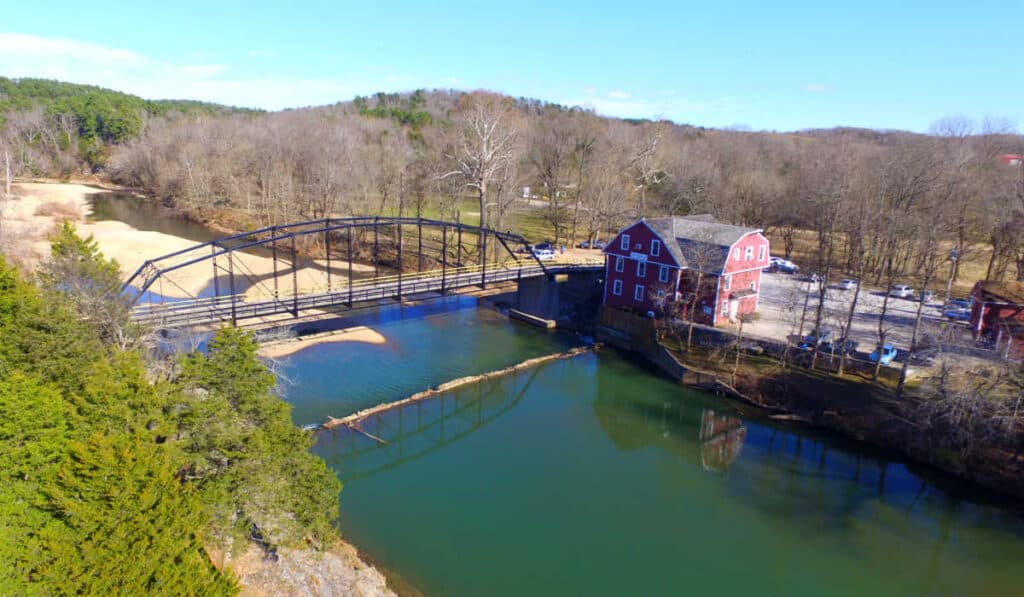
Rivers, Streams, and Lakes
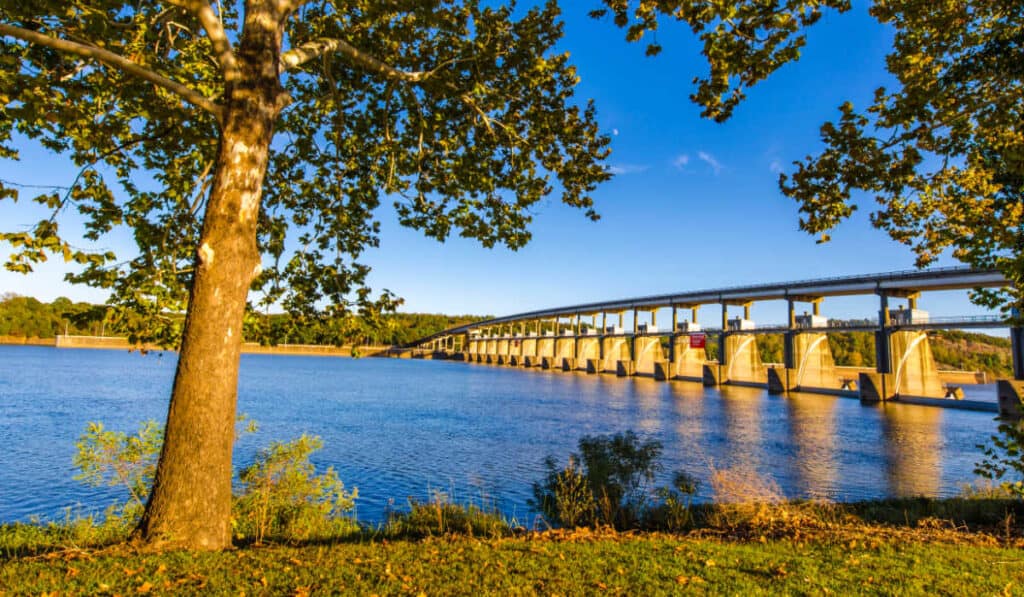
The Ozarks are home to numerous rivers, streams, and lakes that contribute to the region’s overall beauty and recreational opportunities. One of the most notable rivers in the area is the Arkansas River, which plays a significant role in shaping the landscape and defining the region’s boundaries. Other important waterways in the Ozarks include the White River, the Buffalo National River, and the Osage River, along with numerous smaller streams and lakes that adorn the region. These water features not only add to the topographical diversity but also provide a habitat for various species of plants and animals, as well as recreational opportunities for visitors and residents alike.
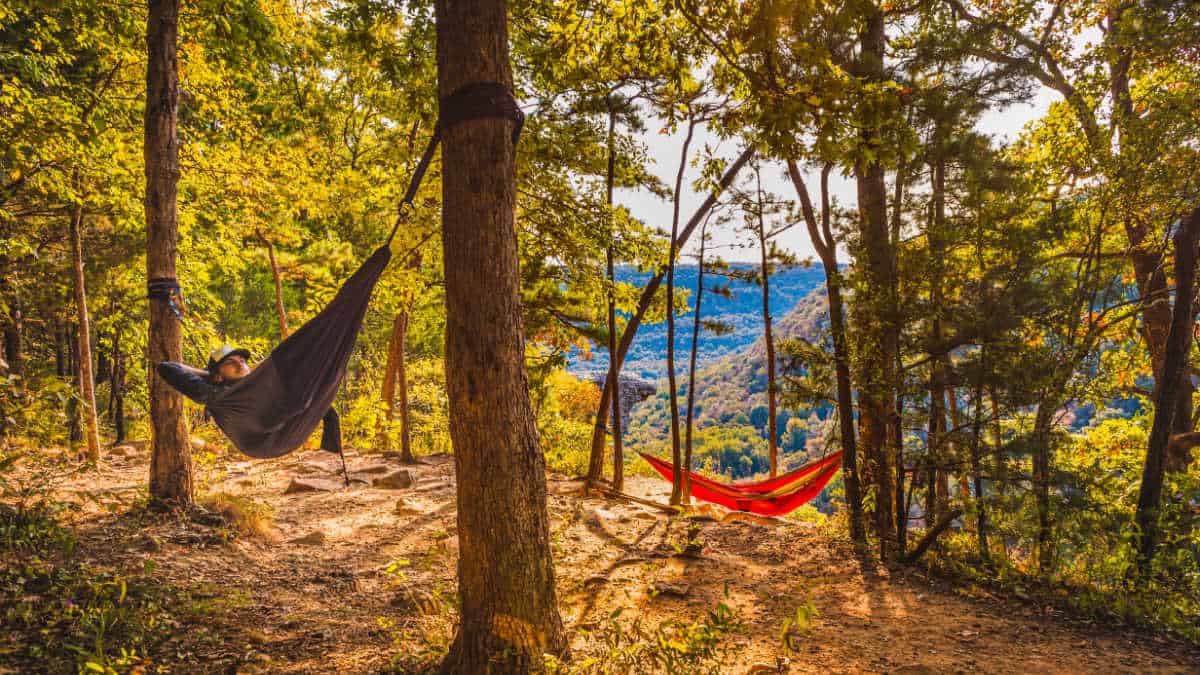
Natural Beauty and Recreation in the Ozark Mountains
The Ozark Mountains, also known as the Ozark Plateau, is an enchanting region known for its natural beauty, diverse plant and animal life, and numerous opportunities for outdoor recreation. This region extends through the states of Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, and a small part of Kansas.
National and State Parks
There are several parks showcasing the beauty of the Ozarks, such as Ozark National Forest in Arkansas. Additionally, the Buffalo National River and the White River offer popular spots for fishing, canoeing, and kayaking. The Ouachita Mountains, a sub-range of the Appalachians, are found in this region as well.
Other nearby parks include the Ozark National Scenic Riverways in Missouri, which is the first national park dedicated to the protection of a river system. This park offers various recreational activities and chances to learn about regional history.
Hiking Trails
The Ozarks boast a vast network of hiking trails suitable for different skill levels, offering picturesque views and varying landscapes. Popular trails include those in the Ozark National Forest and the Ouachita National Forest, which contain numerous paths to explore and admire the unique geology, forests, and water features of the region.
Wildlife and Plant Life
This region provides a perfect habitat for a diverse range of flora and fauna. Wildlife commonly seen in the Ozarks includes white-tailed deer, wild turkeys, and black bears, among other native species. The diverse plant life is characterized by various forms of trees, shrubs, and wildflowers.
Waterfalls and Natural Springs
The Ozarks are also home to several stunning waterfalls and natural springs that draw visitors from all over the world. Some of the most popular locations include Hedgehog Waterfall, Amethyst Falls, and many others. These locations make perfect spots for swimming, photography, or simply admiring the natural beauty of the region.
The Ozark Mountains offer a mix of breathtaking landscapes, unique geological formations, and diverse wildlife, making it a prime tourist destination. Whether you’re an experienced hiker, a casual camper, or just looking to explore nature’s beauty, the Ozarks have something for everyone.
Ecology and Natural Resources of the Ozarks
The Ozark Mountains, also known as the Ozark Plateau, are an ancient and rich natural region located in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, and the southeastern corner of Kansas. The ecology and natural resources of this region include forests, minerals, and agricultural land.
Forests and Timber
The Ozarks are heavily forested, predominantly with oak and hickory trees. The forests here provide valuable timber, such as black walnut, cherry, and maple, which is harvested for the lumber industry. These forests are home to numerous species of animals, including deer, black bears, and various types of birds. Additionally, the Ozarks contain multiple caves and springs, such as Eureka Spring, which is a popular tourist destination due to its curative waters.
Minerals and Mining
Historically, the Ozark Mountains have been a significant source of minerals, particularly iron and lead. The U.S. Interior Highlands in this region are rich in these minerals, leading to a long history of mining activity. While mining has declined in recent years, the area is still rich in mineral resources, including zinc, barite, and limestone.
Agriculture and Land Use
Agriculture plays a crucial role in the Ozarks’ economy. Given the land’s general fertility and availability of water resources, it is apt for various agricultural activities. The uplifted level plateaus are mostly utilized for raising crops such as corn, soybeans, wheat, and hay. The region is also well known for fruit production, particularly apples, peaches, and grapes. Additionally, livestock such as cattle, hogs, and poultry are raised in the Ozarks, contributing significantly to the local economy.
The Ozark Mountains offer an extraordinary range of natural resources and are crucial to the economy and ecology of the region. By understanding and managing these resources, the communities can continue to grow and thrive while preserving the natural beauty of the area.
Ozark Mountain Culture and History
Indigenous History
The Ozark Mountains have a rich indigenous history, primarily involving Native American tribes. Long before European settlers arrived, various tribes including the Osage, Caddo, and Quapaw inhabited this region across Missouri, Arkansas, Oklahoma, and southeastern Kansas. These tribes established their own unique cultures, traditions, and languages, all deeply intertwined with the natural environment of the Ozarks.
Settlement and Development
European settlers began to arrive in the Ozarks in the early 19th century, with many migrating from the southeastern United States. As communities developed in towns like Eureka Springs, Fayetteville, and Branson, these settlers heavily influenced the region’s distinctive culture and society. By the late 19th century, the Ozarks had also developed into an important hub of regional trade, as the railroad industry expanded and connected the area with major surrounding cities.
The role of natural resources and agriculture in Ozark communities has remained crucial throughout the region’s development. Logging, mining, and farming have all played important parts in shaping the economies and lifestyles of the people who live there.
Influences on Art and Music
The Ozarks have made significant contributions to art and music within the United States. Traditional Ozark music reflects the region’s Celtic and Appalachian heritage, blending elements of folk, bluegrass, and gospel to create a distinct regional sound. Furthermore, the rugged beauty of the Ozarks has also provided artists with an abundance of inspiration for their visual art, often capturing breathtaking landscapes and the raw spirit of the region’s early settlers.
Artists, musicians, and writers from the Ozarks have gained national and international recognition for their works, further enriching the cultural landscape of the area. Festivals, museums, and galleries throughout the region showcase its vibrant contribution to American arts and culture.